You need to know the major differences between VPN vs. DNS Proxy(smart DNS) so that you can choose the right service to meet your needs.
When you search for the comparison of VPN vs. DNS Proxy (smart DNS), you may find most articles are over-simplified or outdated.
This post tries to explain the differences between VPN vs. DNS Proxy (smart DNS) in depth from the following 7 distinct perspectives: location spoofing, traffic encryption, speed, security, cost, ease of use, and additional features.
Table of Contents
- Why and when do you need to use VPN or DNS proxy (smart DNS)?
- VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): the summary
- VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Location spoofing
- VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Traffic encryption
- VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Speed
- VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Security features
- VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Additional features
- VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Cost
- VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Ease of use
- VPN vs. DNS Proxy (Smart DNS): what are your thoughts?
Why and when do you need to use VPN or DNS proxy (smart DNS)?
In today’s digital age, it’s essential to protect your online privacy and access geo-restricted content. Two popular technologies used for this purpose are Smart DNS and VPN.
While both Smart DNS and VPN can help you bypass geo-restrictions and protect your online privacy, they work in different ways.
What is Smart DNS?
DNS proxy, aka Smart DNS, is a technology that allows you to bypass geographic restrictions on content by changing the DNS server that your device uses to resolve domain names.
DNS stands for Domain Name System, which is the protocol that translates domain names into IP addresses. When you type a website’s domain name into your browser, your device sends a request to a DNS server to resolve the domain name into an IP address. Once the IP address is obtained, your device connects to the website’s server using that IP address.
Smart DNS works by changing the DNS server that your device uses to resolve domain names. Instead of using your ISP’s DNS server, which may be restricted in terms of the content it can access, Smart DNS allows you to use a different DNS server that can access content that is blocked in your region (i.e., bypass geo-restrictions). By doing so, you can access content that is otherwise unavailable in your area.
For example, suppose you’re located in the US, and you want to access content that’s only available in the UK, such as BBC iPlayer. If you try to access BBC iPlayer from the US, you’ll get an error message that the content is unavailable in your region. However, if you use a Smart DNS service, you can change your DNS server to a UK-based server, and BBC iPlayer will think that you’re accessing the content from the UK. As a result, you’ll be able to access the content as if you were physically located in the UK.
The following graph illustrates how DNS proxy works.
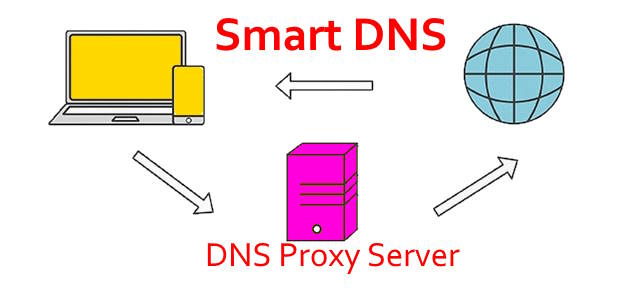
Smart DNS does not encrypt your internet traffic or change your IP address. It only spoofs your location by making it appear as if you’re accessing the content from a different region. As a result, your internet traffic may not be secure, and your ISP can still see your online activities. However, if your primary goal is to access geo-restricted content, Smart DNS can be a convenient and fast solution.
What is VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network, and it’s a technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet.
When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic is routed through an encrypted tunnel to a remote server, which then sends the traffic out to the internet. This makes it much harder for anyone to intercept or monitor your online activities, as your traffic is encrypted and your IP address is hidden.
The following picture illustrates how VPN works.
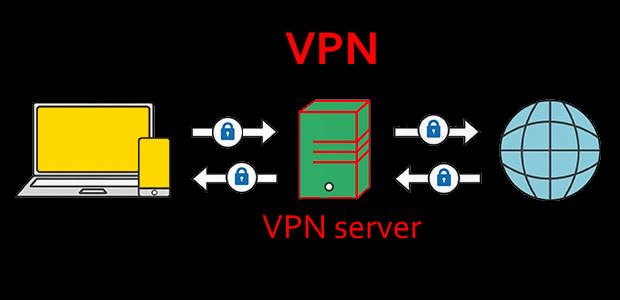
VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): the summary
DNS Proxy (Smart DNS) is primarily designed to help you bypass geo-restrictions and access content that’s not available in your region. It spoofs your location by changing the DNS server that your device uses to resolve domain names. However, it does not encrypt your internet traffic or change your IP address, so your online activities are still visible to your ISP and other third parties.
VPN, on the other hand, provides a more comprehensive solution for online privacy and security. It encrypts your internet traffic, hides your IP address and location, and provides additional security features such as ad-blocking and malware protection. However, VPN is slower than Smart DNS due to the encryption overhead, and it may not be the best option if your primary goal is to access geo-restricted content quickly.
In summary, DNS proxy (Smart DNS) and VPN are both useful technologies that can help you protect your online privacy and access content that’s not available in your region. Smart DNS is a fast and convenient solution for accessing geo-restricted content, while VPN provides a more comprehensive solution for online privacy and security. So, the choice between VPN vs. DNS proxy (Smart DNS) depends on your specific needs and priorities.
VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Location spoofing
When you use the internet, your device sends requests to servers located all around the world to access websites, apps, and other online services. To send these requests, your device needs to know the IP address of the server it’s communicating with.
IP addresses are like the postal addresses of the internet. They uniquely identify every device that’s connected to the internet and allow them to send and receive data. However, IP addresses are also used to determine your approximate location.
Location spoofing is the process of tricking websites and online services into thinking that you’re accessing them from a different location than you actually are. This is typically done by changing the IP address that your device sends to the website or online service.
DNS proxy (Smart DNS) is one way to spoof your location. When you use a Smart DNS service, your device sends DNS queries to a different DNS server than the one provided by your ISP. This DNS server is specially configured to return IP addresses that correspond to servers located in a different region than your actual location.
For example, if you’re located in the US and want to access content that’s only available in the UK, you can use a Smart DNS service that provides a UK DNS server. When you try to access the content, your device sends a DNS query to the UK DNS server instead of your ISP’s DNS server. The website or online service sees the request from a UK IP address and assumes that you’re located in the UK, allowing you to access the content.
It’s important to note that DNS proxy (Smart DNS) only spoofs your location for DNS queries. It does not encrypt your internet traffic or change your IP address for other types of requests. As a result, your actual location may still be visible to third parties who are monitoring your internet traffic.
VPN is another way to spoof your location. When you use a VPN service, your device encrypts all of your internet traffic and sends it through a VPN server located in a different region than your actual location. The VPN server decrypts your traffic and sends it to the website or online service on your behalf. This is similar to a web proxy.
For example, if you’re located in the US and want to access content that’s only available in the UK, you can connect to a VPN server located in the UK. All of your internet traffic is encrypted and sent to the UK VPN server, which then sends it to the website or online service. The website or online service sees the UK IP address of the VPN server and assumes that you’re located in the UK, allowing you to access the content.
VPN provides a more comprehensive solution for location spoofing than Smart DNS, as it encrypts all of your internet traffic and changes your IP address for all types of requests. This makes it a more secure option for accessing geo-restricted content and protecting your online privacy.
VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Traffic encryption
When you use the internet, all of your online activities involve sending and receiving data between your device and servers located all around the world. This data can include sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, personal information, and more.
Unfortunately, this data is not inherently secure. It can be intercepted and read by third parties who are able to intercept your internet traffic. This includes your internet service provider (ISP), government agencies, hackers, and other malicious actors.
Traffic encryption is the process of encoding your internet traffic so that it can’t be intercepted or read by unauthorized third parties. Encryption works by converting your data into a code that’s unreadable without the right key to decrypt it.
When you use a VPN service, all of your internet traffic is encrypted before it leaves your device and is sent to the VPN server. The VPN server decrypts your traffic and sends it to its intended destination. This means that anyone who intercepts your internet traffic will only see a jumbled mess of letters and numbers rather than your actual data.
VPN encryption typically uses one of two protocols: OpenVPN or IPSec. Both protocols use advanced encryption algorithms to ensure that your data is secure. The encryption level is typically measured in bits, with higher numbers indicating stronger encryption. A typical VPN encryption level is 256-bit, which provides a very high level of security.
Smart DNS, on the other hand, does not encrypt your internet traffic. Since Smart DNS only spoofs your location for DNS queries, it does not need to encrypt your data. This means that your internet traffic is still visible to your ISP and other third parties who are monitoring your internet activity.
In short, VPN provides strong traffic encryption to protect your data from prying eyes, while Smart DNS does not encrypt your internet traffic. If you’re looking for a solution to protect your online privacy and keep your data secure, VPN is generally the better option due to its comprehensive security features.
VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Speed
In terms of overall speed, a DNS proxy (Smart DNS) is generally faster than VPN. This is because Smart DNS only routes your DNS queries through a remote server while your internet traffic still flows directly to its intended destination. This means that there’s less overhead involved in processing your internet traffic, which can result in faster overall speeds.
On the other hand, VPN does encrypt your internet traffic and routes it through a remote server. This additional processing can cause some slowdown in internet speed, especially if you’re connecting to a VPN server that’s located far away from your physical location. However, the speed reduction is typically minimal and may not be noticeable for most online activities.
It’s worth noting that there are many factors that can impact internet speed, regardless of whether you’re using Smart DNS or VPN. Some of the most common factors that can impact internet speed include:
- Distance to the server: The closer you are physically located to the server, the faster your internet speed will be.
- Internet connection quality: A faster internet connection will typically result in faster internet speeds.
- Server load: If a server is experiencing high levels of traffic, it may slow down your internet speeds.
- Device performance: Older or less powerful devices may struggle to keep up with demanding internet activities, which can impact internet speed.
Ultimately, the speed difference between VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS) will depend on your individual circumstances. If speed is a top priority for you, then Smart DNS may be a better option. However, if security and privacy are more important, then VPN is likely the better choice, despite any potential speed reduction.
VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Security features
Smart DNS (DNS proxy) provides minimal security features. The primary function of Smart DNS is to bypass geo-restrictions and unblock content, and it doesn’t offer any encryption or privacy protection beyond hiding your DNS queries. While this can be helpful for accessing regionally-restricted content, it doesn’t provide any protection against hackers or other online threats.
In contrast, VPN offers a robust set of security features. VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it more difficult for third parties to intercept or eavesdrop on your online activities. This can be especially important if you’re using public Wi-Fi networks, which can be vulnerable to hacking and other security threats.
In addition to encryption, many VPN services also offer features like:
- Kill switch: This is a security feature that automatically disconnects your internet connection if the VPN connection drops, preventing any unencrypted traffic from leaking out.
- Malware protection: Some VPN services offer built-in malware protection to help protect your device from viruses, spyware, and other online threats.
- Ad blocking: Some VPN services also offer ad-blocking features, which can help to improve your online browsing experience and reduce the risk of being exposed to malicious ads.
Overall, VPN is a more secure option than Smart DNS, and it offers a range of features to help protect your online privacy and security. While Smart DNS can be useful for accessing regionally-restricted content, it doesn’t provide any significant security benefits beyond hiding your DNS queries.
VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Additional features
Let’s check some additional features.
Multi-platform support
Both DNS proxy and VPN services are available for a wide range of platforms, including Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and Linux. This means that you can use a VPN on almost any device, including desktops, laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
In fact, a DNS proxy can be easily set up in your router and make it works on all connected device automatically. You do not need to do anything on your devices.
Anonymous browsing
VPNs allow you to browse the internet anonymously by masking your IP address and encrypting your internet traffic. This can help to protect your privacy and prevent your online activities from being tracked by third parties.
Torrenting support
Many VPN services allow you to download and share files via P2P (peer-to-peer) networks. This can be useful if you frequently download large files, such as movies or music, and want to protect your privacy while doing so.
Access to blocked content
In addition to bypassing geo-restrictions, VPNs can also be used to access content that may be blocked by your ISP or other entities. This can include social media sites, news websites, and other content that may be restricted in your region.
DNS proxy (Smart DNS) is useless if you want to access contents blocked by your ISP.
Dedicated IP address
Some VPN services offer dedicated IP addresses, which can be useful if you need to access a specific website or service that requires a consistent IP address.
VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Cost
Cost is an important factor to consider when choosing between Smart DNS and VPN.
Overall, while Smart DNS services are generally less expensive than VPNs, it’s important to consider your specific needs and prioritize your online privacy and security.
If you’re mainly interested in accessing regionally-restricted content, a Smart DNS service may be sufficient and more affordable. But if you want the added protection of encryption and anonymous browsing, a VPN may be a worthwhile investment.
VPN vs. DNS proxy (smart DNS): Ease of use
When it comes to ease of use, VPN vs. DNS proxy (Smart DNS) each have their own strengths and weaknesses.
Smart DNS:
- Smart DNS services are generally easier to set up and use than VPNs. Once you’ve signed up for a Smart DNS service and updated your device’s DNS settings, you can start accessing regionally-restricted content right away. There are usually no additional steps required to connect to the service or configure settings.
- Smart DNS services can also be used on a wider range of devices than VPNs. Many Smart DNS services offer setup guides and tutorials for a variety of devices, including gaming consoles, smart TVs, and other devices that may not be compatible with VPNs.
VPN:
- While VPNs may be more complex to set up and configure than Smart DNS, many VPN providers offer user-friendly apps that make it easy to connect to the service and change settings. With a few clicks or taps, you can connect to a VPN server, change your virtual location, and adjust other settings.
- VPNs are also more versatile than Smart DNS in terms of the features they offer. In addition to content unblocking, VPNs provide encryption, anonymous browsing, and other features that can help to protect your online privacy and security.
Overall, Smart DNS is generally easier to use and set up than VPNs. However, if you’re willing to invest a little time in configuring a VPN, you’ll get access to a wider range of features and greater security and privacy protection. It’s important to consider your priorities and needs when choosing between Smart DNS and VPN, and to choose a service that provides the right balance of ease of use, features, and protection.
VPN vs. DNS Proxy (Smart DNS): what are your thoughts?
Please share your thoughts on VPN vs. DNS Proxy (Smart DNS) in the comment box below.
You can reach us through the following:
- From our Facebook page
- Contact Us page.
Safe surging!

Leave a Reply